Description
Description
Human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6) is the common collective name for Human herpesvirus 6A (HHV-6A) and Human herpesvirus 6B (HHV-6B). These closely related viruses are two of the nine herpesviruses known to have humans as their primary host. HHV-6A and HHV-6B are double stranded DNA viruses within the betaherpesvirinae subfamily and of the genus Roseolovirus. HHV-6A and HHV-6B infects almost all of the human populations tested. The overall nucleotide sequence identity between HHV-6A and HHV-6B is 90% and they are now classified as distinct species.
HHV-6A has been described as more neurovirulent, and as such is more frequently found in patients with neuroinflammatory diseases such as multiple sclerosis.
HHV-6B primary infection is the cause of the common childhood illness exanthem subitum (also known as roseola infantum or sixth disease). Additionally, HHV-6B reactivation is common in transplant recipients, which can cause several clinical manifestations such as encephalitis, bone marrow suppression and pneumonitis.
gQ1 encoded by the U100 gene of HHV6 is glycoprotein, complexes with gH, gL and gQ2 to form HHV6A ligand to CD46 receptor and HHV6B ligand to CD134 receptor. It is expressed in two different forms: an 80-kDa form (gQ1-80K) and a 74-kDa form (gQ1-74K) – only gQ1-80K, but not gQ1-74K, forms the ligand complex with gQ2, gH, and gL. It associates with lipid rafts.
Applications
- Western blot 1:500-1,000 dilution
- Immunoprecipitation (assay dependent)
- Imunofluorescence staining and Immunocytochemistry 1:100-3,200 dilution
- Flow Cytometry 1:100
- ELISA (assay dependent)
Specification
Immunogen: His6-tagged recombinant gQ1 of HHV-6A encoding 3-422 amino acids expressed in E. coli.
Specificity: Reacts with gQ1 of HHV6A and HHV6B
Isotype: mouse IgG1 kappa
Product: Produced in serum-free medium and purified by proprietary chromatography procedure under mild conditions. 90~95% pure by SDS-PAGE.
Form: 1 mg/ml in PBS, 50% glycerol, filter sterilized. Sodium azide and carrier-free.
Storage: Ship at 4°C or -20°C, and upon arrival, centrifuge, and store at -20°C.
References: This antibody has been described in Ref. 1 and used the following publications.
- Mori Y. et al. (2003) The Human Herpesvirus 6 U100 Gene Product Is the Third Component of the gH-gL Glycoprotein Complex on the Viral Envelope. Virol. 77: 2452-2458. PubMed 12551983 Free Article. WB, IP
- Mori Y. et al (2003) Human Herpesvirus 6 Variant A Glycoprotein H-Glycoprotein L-Glycoprotein Q Complex Associates with Human CD46. J. Virol. 77: 4992-4999. PubMed 12663806 Free Article. WB, IP
- Mori Y. et al. (2004) Discovery of a second form of tripartite complex containing gH-gL of human herpesvirus 6 and observations on CD46. J Virol. 78:4609-16. PubMed 15078943. Free Article. WB, IP
- Akkapaiboon P. et al. (2004) Intracellular processing of human herpesvirus 6 glycoproteins Q1 and Q2 into tetrameric complexes expressed on the viral envelope. J Virol. 78:7969-83. PubMed 15254169 Free Article. WB, IP, IF
- Huang et al (2006) Human herpesvirus 6 envelope cholesterol is required for virus entry. J Gen Virol. 87: 277-285. PubMed 16432012 Free Article. WB, Flow Cyt.
- Tang H. et al. (2010) Human herpesvirus 6 encoded glycoprotein Q1 gene is essential for virus growth. 407:360-7. PubMed 20863544 Free Article. WB
- Tang H. et al (2011) Human herpesvirus 6 glycoprotein complex formation is required for folding and trafficking of the gH/gL/gQ1/gQ2 complex and its cellular receptor binding. J Virol. 85:11121-30. PubMed 21849437 Free Article. WB, IP, Flow Cyt.
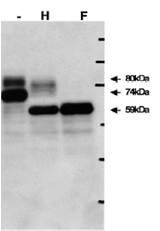
Fig.1. Identification of gQ1 in HHV-6A infected cells by Western blot using anti-gQ antibody (119).
T-cell line HSB-2 cells were infected with HHV-6A at m.o.i of 0.1 and the cells were harvested at 72 h post infection for lysate preparation for WB. gQ1 is detected as two glycoproteins with 80 kDa and 74 kDa molecular masses.
Sample lysates: (-) Non-treated, (H) Treated with end-glycosilase H, (F) Treated with peptide N-glycosidase F.
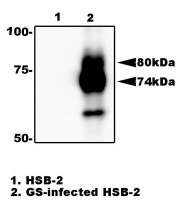
Fig.2. Immunoprecipitation of gQ1 from HHV-6A infected cell lysate with anti-gQ1 antibody (119). gQ1 protein was precipitated from the lysate of infected HSB-2 cells by using agarose beads-conjugated anti-gQ1 antibody (119), and processed for Western blot by using anti-gQ1 antibody (119). Lane 1; HSB-2 cells. Lane 2; HSB-2 cells infected with HHV-6A GS strain
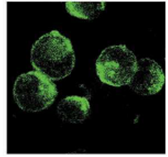
Fig.3. Immuno-staining of gQ1 in HHV6A infected HSB-2 cells by using anti-gQ1 antibody.
The infected cells were harvested 3 days post infection, fixed in cold acetone and immunostained with FITC-conjugated anti-gQ1 antibody (119). Specific immunofluorescence was observed with a confocal laser scanning microscope.
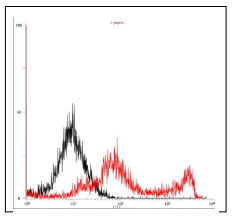
Fig.4. Flow cytometry analysis of gQ1 expression on the cell surface in a transient expression system. 293T cells were transfected with gQ1 expression plasmid. The cells were harvested on second day postinfection, fixed with 4% PFA, permeabilized with 0.1% Triton-X100, incubated with anti-gQ1 antibody (119) and then with FITC-conjugated anti-mouse IgG antibody. Histograms show fluorescence intensities measured in arbitrary units on a log scale (x axis) and relative cell numbers on a linear scale (y axis). Black line is control and red line is gQ1 introduced cells.



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.